NEJM Healer offers a systematic way to develop clinical reasoning skills through deliberate practice.
NEJM Healer packages the most current and reliable clinical information in an expansive library of patient cases with a granular, data-driven approach to building skills.
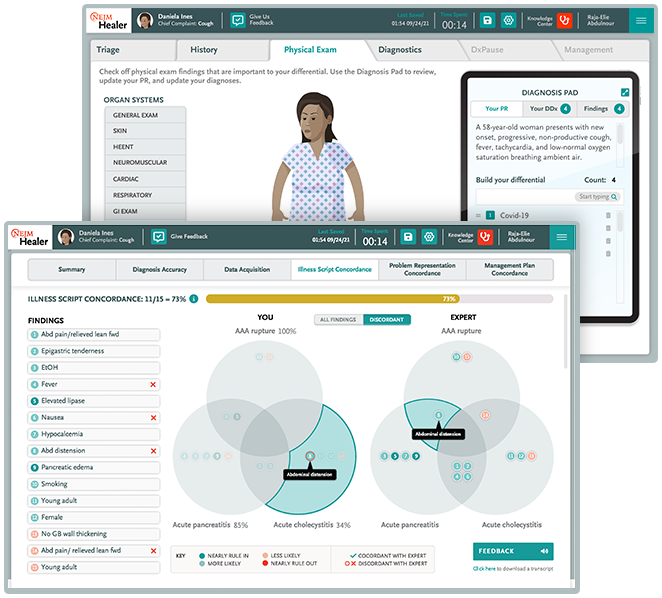
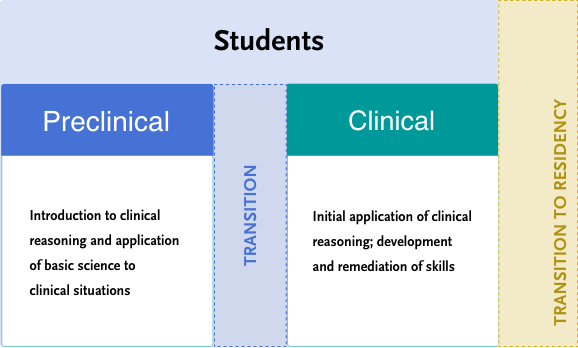
Using NEJM Healer, students engage in simple, yet immersive virtual patient encounters. They learn how to thoroughly gather and evaluate data, iteratively create problem representations, activate illness scripts, build broad differential diagnoses, and apply knowledge to home in on a lead diagnosis and outline a sound management plan.
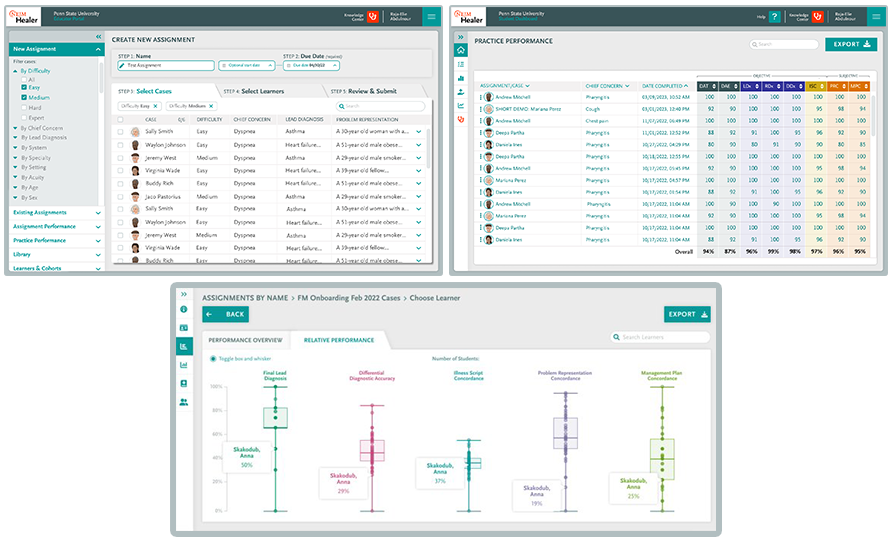
Educators can monitor a student’s path to sound clinical reasoning through a digital fingerprint of each student’s data-gathering and decision-making history, helping them to identify students in need of remediation, and informing their evaluations.